
Question: What is largest the single-cell organism? Is it a bacterial cell?Īnswer: Caulerpa taxifolia is regarded as the largest single-cell organism that can grow to a length of six to twelve inches. Other microorganisms are archaea, protists, and certain fungi. Microorganisms are organisms that are microscopic, and thus, individual cells of bacteria can be seen using a microscope. Question: What are microorganisms? Are bacteria microorganisms?Īnswer: Yes, bacteria are microorganisms. Question: are bacteria unicellular or multicellular organisms?Īnswer: Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can live independently. Question: Are bacteria prokaryotic or eukaryotic?Īnswer: Bacteria are characteristic prokaryotic organisms. Note: the word “bacteria” is the plural form of bacterium, not “bacterias”. Question: What is the singular form of bacteria?Īnswer: Bacterium. Before proceeding any further, let’s answer some of the basic questions about bacteria.
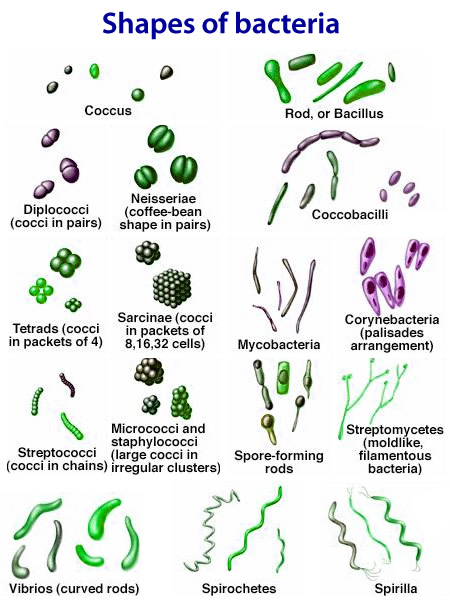
#Different types of bacteria shapes and info how to
Now, we know how to define bacteria and the meaning of bacteria. They play a variety of important roles in the ecosystem such as breaking down the toxic components, recycling the nutrients, fixing nitrogen in the soil from the air, among many others.įigure 1: Bacteria Cell Diagram. Most bacteria, barring a few, are beneficial for their environment. They are structurally simple but functionally complex organisms that form the basis of all life on earth. What are bacteria? What is the definition of bacteria in biology? Bacteria are defined as organisms that are microscopic, unicellular, independently reproducing, and mostly free-living.

In other words, two organisms in a differentially stained sample may appear to be different colors. In contrast, differential staining distinguishes organisms based on their interactions with multiple stains.
A simple stain will generally make all of the organisms in a sample appear to be the same color, even if the sample contains more than one type of organism. In simple staining, a single dye is used to emphasize particular structures in the specimen. Some staining techniques involve the application of only one dye to the sample others require more than one dye. Commonly used acidic dyes include acid fuchsin, eosin, and rose bengal. On the other hand, the negatively charged chromophores in acidic dyes are repelled by negatively charged cell walls, making them negative stains. Thus, commonly used basic dyes such as basic fuchsin, crystal violet, malachite green, methylene blue, and safranin typically serve as positive stains. (credit a: modification of work by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention credit b: modification of work by Roberto Danovaro, Antonio Pusceddu, Cristina Gambi, Iben Heiner, Reinhardt Mobjerg Kristensen credit c: modification of work by Anh-Hue Tu)īecause cells typically have negatively charged cell walls, the positive chromophores in basic dyes tend to stick to the cell walls, making them positive stains. megaterium appear to be white because they have not absorbed the negative red stain applied to the slide. (b) This specimen of Spinoloricus, a microscopic marine organism, has been stained with rose bengal, a positive acidic stain.

\): (a) These Bacillus anthracis cells have absorbed crystal violet, a basic positive stain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
